getDesignGroupSequential()
getDesignInverseNormal()
getDesignFisher()
getDesignConditionalDunnett()Getting started with rpact
November 3, 2025
Quick Intro
Welcome to this rpact workshop! 🎉
- This is the first time we offer this workshop publicly
- We are happy to have you here! 😄
- Feel free to ask questions at any time using the Zoom Q&A or chat function
- Please participate in the Zoom poll so we can get to know your background a little bit
Daniel

- Ph.D. in Statistics from University of Zurich, Bayesian Model Selection
- Biostatistician at Roche for 5 years, Data Scientist at Google for 2 years, Statistical Software Engineer at Roche for 4 years
- Co-founder of RCONIS
- Multiple R packages on CRAN and Bioconductor, co-wrote book on Likelihood and Bayesian Inference, chair of
openstatsware - Feel free to connect
Friedrich
- Computer scientist (Diploma/M.Sc.) with a Ph.D. in Human Biology focusing on biostatistics from the University of Lübeck, Germany
- Independent consultant in computer science, data science, and biostatistics since 2008
- Co-founder and CEO of RPACT, a company developing the formally validated R package rpact with 31 releases on CRAN since 2018
- Co-founder of RCONIS
- Software architect, R programmer since 2004, and Shiny developer since 2019
- Feel free to connect at LinkedIn or Github

RCONIS 🚀
- Statistical consulting and engineering services:
Research Consulting and Innovative Solutions - Grow RPACT company to offer a wider range of services
- Strengthen maintainer team for the
rpactpackage - Website: rconis.com
- Check out our this summer’s birthday blog post 🎂
RCONIS Team

What you will learn today
- Understand the basics about
rpact - Get to know the graphical user interface RPACT Cloud
- Go through a practical example of clinical trial design using
rpact
What you will need
- Your own R installation with
rpactinstall.packages("rpact")
- Access to RPACT Cloud via cloud.rpact.com
The R Package rpact – Functional Range

Trial Designs
- Fixed sample design
- Group sequential designs
- Adaptive designs using the inverse normal and Fisher’s combination test, and conditional error rate principle
Easy to understand R commands:
Sample Size and Power Calculation
for
- testing means (continuous endpoint)
- testing rates (binary endpoint)
- survival trials with flexible recruitment and survival time options
- testing rates for count data
Easy to understand R commands:
Example:
Adaptive Analysis
for testing means, rates, and survival data
- Calculates adjusted point estimates and confidence intervals
- Some highlights:
- Automatic boundary recalculations during the trial for analysis with alpha spending approach, including under- and over-running
- Adaptive analysis tools for multi-arm trials
- Adaptive analysis tools for enrichment design
Easy to understand R commands:
…
Simulation Tool
for means, rates, survival data, and count data
- Assessment of adaptive sample size/event number recalculation strategies
- Assessment of treatment selection strategies in multi-arm trials
- Assessment of population selection strategies in enrichment designs
Easy to understand R commands:
Example:
\(\rightarrow\) rpact useful for conducting flexible simulations in clinical trial planning
User Concept – R generics
In general, everything runs with the R standard functions which are always present in R: so-called R generics.
- Visualize:
print()summary()plot()
- Continue work:
as.data.frame()length()names()
User Concept – Most parameters have a default value
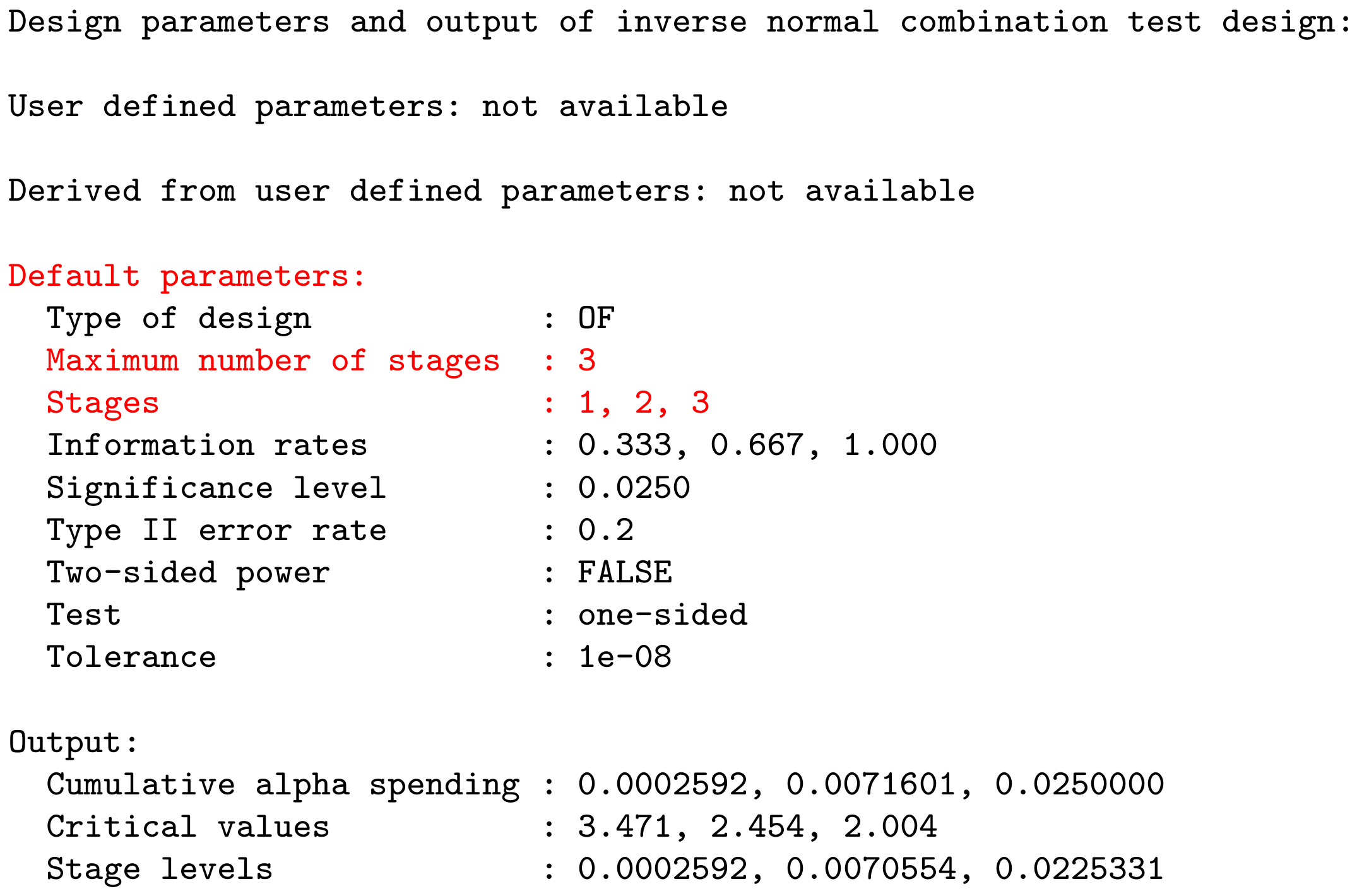
Example: getDesignInverseNormal() produces the output:
User Concept – Most parameters have a default value
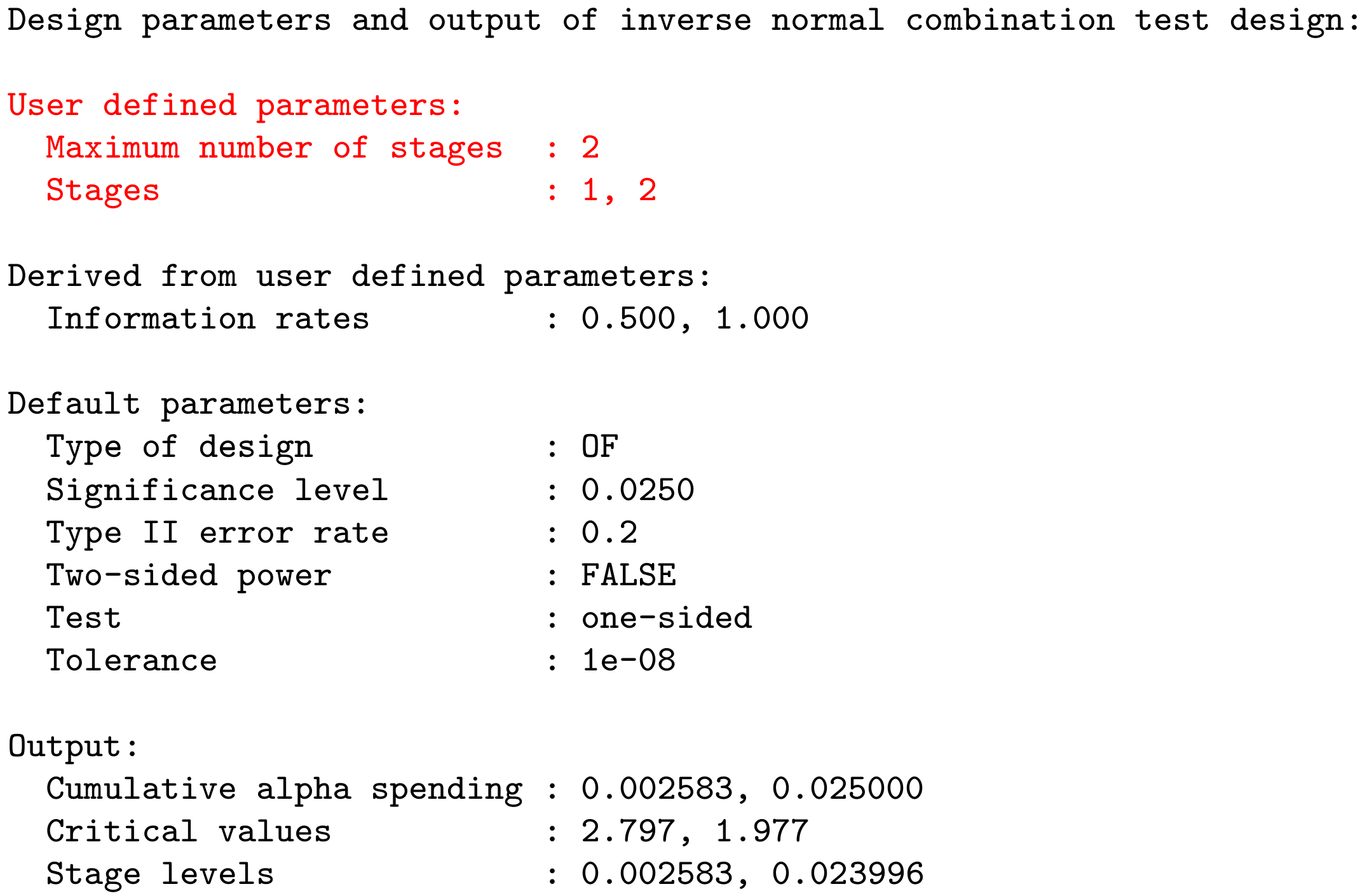
Example: getDesignInverseNormal(kMax = 2) produces the output:
User Concept – Support of pipe operators
Analysis results (means of one group, group sequential design)
Design parameters
- Information rates: 0.333, 0.667, 1.000
- Critical values: 3.471, 2.454, 2.004
- Futility bounds (non-binding): -Inf, -Inf
- Cumulative alpha spending: 0.0002592, 0.0071601, 0.0250000
- Local one-sided significance levels: 0.0002592, 0.0070554, 0.0225331
- Significance level: 0.0250
- Test: one-sided
Default parameters
- Normal approximation: FALSE
- Direction upper: TRUE
- Theta H0: 0
Stage results
- Cumulative effect sizes: 45.00, 48.60, 47.25
- Cumulative (pooled) standard deviations: 130.0, 134.8, 128.7
- Stage-wise test statistics: 1.548, 1.995, 2.054
- Stage-wise p-values: 0.06905, 0.02774, 0.02455
- Overall test statistics: 1.548, 2.550, 3.285
- Overall p-values: 0.0690533, 0.0069750, 0.0007617
Analysis results
- Assumed standard deviation: 128.7
- Actions: continue, reject and stop, reject
- Conditional rejection probability: 0.08839, 0.50232, NA
- Conditional power: NA, NA, NA
- Repeated confidence intervals (lower): -76.25044, 0.08653, 17.95726
- Repeated confidence intervals (upper): 166.25, 97.11, 76.54
- Repeated p-values: 0.2531791, 0.0247936, 0.0007821
- Final stage: 2
- Final p-value: NA, 0.00708, NA
- Final CIs (lower): NA, 9.421, NA
- Final CIs (upper): NA, 84.18, NA
- Median unbiased estimate: NA, 46.82, NA
The R Package rpact – Getting started
Various learning concepts available:
- Training, online or onsite: www.rpact.com/contact
- Vignettes: www.rpact.org/vignettes
- Graphical user interface RPACT Cloud: cloud.rpact.com
RPACT Connect
- All important information and resources about RPACT on one dashboard page
- Customer-specific resources, e.g.,
- training slides,
- annual meeting slides, and
- the rpact validation documentation
- Use RPACT Connect to jump to RPACT Cloud and unlock advanced features
- Sign up: Please use your corporate email address so RPACT Connect can recognize and load your organization specific resources automatically
- RPACT Connect: connect.rpact.com
The R Package rpact - Online Resources
Further information, installation, and usage:
- CRAN: cran.r-project.org/package=rpact
- GitHub Pages: docs.rpact.org/
- GitHub: github.com/rpact-com/rpact
- OpenSci R-unisverse: rpact-com.r-universe.dev/rpact
- METACRAN: r-pkg.org/pkg/rpact
- Codecov: app.codecov.io/gh/rpact-com/rpact
- RPACT manual and vignettes: rpact.org
- RPACT validation and training: rpact.com
New Edition of the Reference Book
- Group Sequential and Confirmatory Adaptive Designs in Clinical Trials by Gernot Wassmer and Werner Brannath
- Second Edition (Springer, 2025) — published on September 24, 2025
- Now featuring numerous rpact R code examples demonstrating the methods implemented in the package
- For more information, visit: link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-89669-9

End of “Getting started with rpact”


